Remember the last time one of your team members missed an important project update, or misunderstood instructions in an email. Now imagine a bigger hiccup like a data breach where some of your company’s sensitive data is exposed. Frustrating, right? That’s why an effective communication policy is essential.
A communication policy governs message clarity, enhances security of company data, and boosts collaboration among team members. However, creating a policy to manage distributed team communication isn’t a walk in the park because there’s no one-size-fits-all formula. While some policy aspects are similar across teams, others must be customized to suffice for your company’s specific needs.
In this guide, we dive deep into communication policy: its benefits and how to create one. We’ll also discuss the challenges you might encounter when implementing a communication policy. Keep reading.
What is Communication Policy?
A communication policy is a set of formal guidelines that outline how information is shared internally and externally within an organization. It defines the methods, channels, and standards for communication to ensure clarity, consistency, and professionalism.
There are two types of communication policy:
1. Internal Communication Policy
An internal communication policy is a set of rules that govern how people within your organization communicate and share information. It outlines how formal and informal communication flows among employees in different departments.
An internal policy defines communication channels employees should use for different types of communication. For example, it may require employees to handle urgent issues via messaging apps like Slack or Chanty. On the other hand, employees can handle non-urgent issues via email or project management software, like ClickUp and Asana.
The policy can also outline expected response times for each message, meeting guidelines, and time zone awareness. The guidelines reduce communication overload, enabling employees to communicate efficiently for seamless collaboration.
2. External Communication Policy
An external communication policy is a set of rules that govern how your employees handle incoming and outgoing information. It outlines how the organization manages information to and from external parties such as customers, clients, media, and the public.
Here are some of the key things the External Communication Policy may include:
- Approved communication channels: It may specify platforms your organization should use for communication. For example, employees should communicate with customers via official company emails and social media accounts.
- Tone of communication: It may guide the tone and style of communication with external parties. For example, employees should communicate in a friendly and professional tone even in the event of disagreements with the client.
- Authorized spokesperson: It will outline who should communicate for your organization with external stakeholders. For example, only the CEO can make statements to the media in a press release during a crisis.
- Response time: It will specify the timeline for responding to external stakeholder complaints, inquiries, and feedback. For example, the customer service representative must respond to customers complaints within two hours.
Key components of an effective Communication Policy
There is no fixed number of elements to include in your communication policy, but there are a few key ingredients that make it effective.
1. Scope
Your communication policy should clearly define its scope. It should outline the types of communication it covers, the department (or teams) it applies to, and channels through which communication will occur. Moreover, the policy should be specific on the audience it applies to, i.e.: employees, partners, external stakeholders, or all of them.
If need be, define the scope of the policy per use case or department. Take an example of a growing remote company with marketing, customer support, and development teams. The policy should clearly define when a guideline applies to the entire team or a specific department.
Additionally, your communication policy should clearly address any exceptions where the rules will not apply. It may allow an employee to bypass standard communication procedures in cases of emergency. For example, instead of an employee writing an official email when dealing with an urgent customer issue, they may have a one-on-one call.
2. Rules on different Communication channels
The next step is deciding which channel is fit for each type of communication. You should also create rules to govern the appropriate use of each channel. The rules will ensure your employees understand when and how to use each type of channel.
Here are some channels, along with examples of rules you can implement:
Emails (e.g. Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo)
- Use email for all formal communication.
- Use a clear subject line in a professional tone.
- Use proper email etiquette. E.g. starting your email with greetings.
Instant Messaging channels (e.g. WhatsApp, Slack, Microsoft Teams)
- Use instant messaging for quick, formal, and informal conversations.
- Maintain professionalism even in informal conversations.
- Use emojis to show a friendly tone without compromising professionalism.
Video conferencing channels (e.g. Zoom, Google Meet, Slack)
- Schedule meetings in advance to give time for preparation.
- Turn off the microphone when not speaking to avoid disrupting the meeting with background noise.
- Follow meeting etiquette, e.g. arrive early and dress respectfully.
Social Media channels (Facebook, TikTok, LinkedIn)
- Avoid posting anything that could ruin a company’s reputation.
- Verify facts before posting.
- Use proper tone and language when posting content.
3. Confidentiality and Security measures
Your communication policy should clearly outline data security guidelines. It should also define how you’ll enforce the rules, and the consequences of contravening the security guidelines.
Some of the measures and guidelines include:
- Use of approved communication channels and tools
- Access control and permissions
- Secure file sharing guidelines
- Password and authentication guidelines
- Phishing and cybersecurity awareness
Ensuring workers follow secure communication guidelines prevents sensitive company or client data from falling into the wrong hands. For example, it mitigates cases of employees accidentally sharing confidential documents in a public channel. Also, making employees encrypt important files and telling them where they must be shared helps follow data privacy laws like HIPAA and GDPR.
4. Response time
Your communication policy should clearly outline how much time it should take to respond to both internal and external communications. For example, employees should respond to internal emails within 24 hours. Or, customer care representatives should attend to customer inquiries within 30 minutes.
Additionally, external policy should define how employees respond to various messages. For example, customer support representatives should acknowledge receipt of the client’s concern. They should update the customer on progress and provide an expected resolution time.
Importance of An Effective Communication Policy
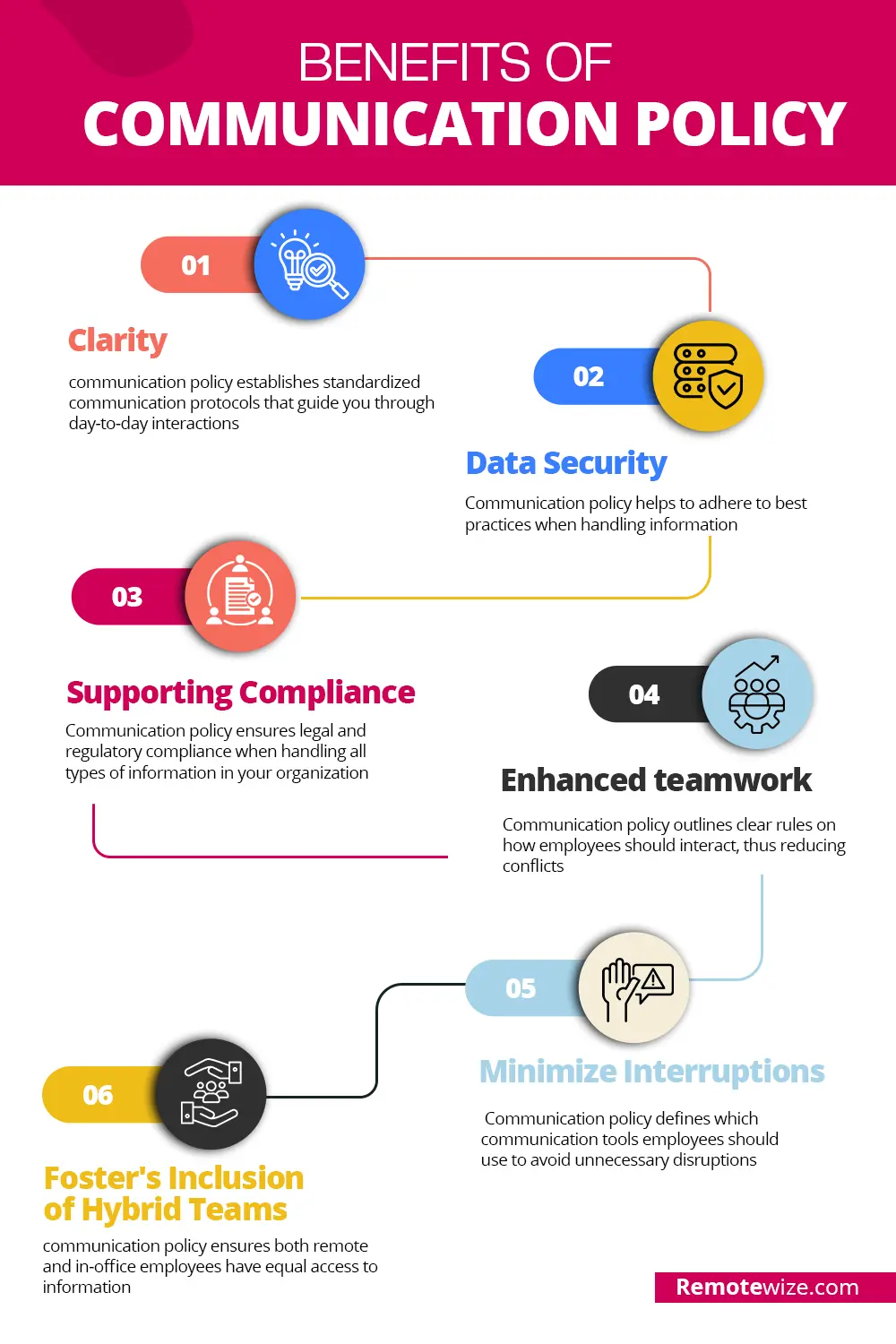
A well-crafted communication policy sets clear expectations on how employees should communicate. It also ensures consistency and collaboration across departments, preventing misunderstanding. Other benefits include:
1. Clarity
Having a well-defined communication policy in your organization fosters clear communication. When communication protocols are clearly defined, employees know how to handle every type of day-to-day interaction.
For example, a policy defines the communication channels employees should use for different interactions. You won’t find employees writing long threads on Slack for an issue that could easily be handled in a quick meeting.
A policy also clearly stipulates the roles and responsibilities of various department leaders, and employees in communication. For example, the HR and compliance team may be responsible for training employees on proper practices. The department can also be tasked with handling sensitive internal and external communications, like terminations and employee disputes.
Defining roles enhances accountability across the team, so everyone knows what is expected of them. This ensures secure, efficient, and professional communication.
Furthermore, a communication policy defines clear timelines for responding to concerns and inquiries. This prevents miscommunication and delays. For example, employees address urgent messages quickly, improving workflow efficiency. Fast, consistent responses can also enhance customer satisfaction and build trust.
2.Data security
A communication policy enhances data security by helping your organization adhere to best practices when handling information. It specifies secure platforms for sharing confidential information, preventing employees from using insecure channels like personal emails.
It also helps enforce role-based access, ensuring each employee has access to data relevant to their role. This prevents sensitive company data from falling into the wrong hands. The policy can also ensure employees adhere to security measures like 2FA. This thwarts unauthorized access to company files and documents.
3. Supporting Compliance
Additionally, a communication policy outlines how your employees should handle sensitive information. For example, you may require employees to share patient information through encrypted channels only. This helps comply with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) regulations.
Moreover, it may outline how employees can report regulatory breaches. Some organizations require employees to report incidents and unethical practices through a private number and other anonymous channels. This makes the work employees feel safe sharing concerns without risking their job or reputation. It helps address non-compliance issues before they escalate.
4. Boosts teamwork
A communication policy establishes clear expectations on how team members interact, collaborate, and share information. Everyone in the organization is aware of the channels to use for different types of communication. For example, email for formal requests, Slack for quick updates, and ClickUp for task tracking.
Doing so minimizes confusion and misunderstanding, ensuring the team stays aligned. In addition, clear response timelines ensure no message is delayed or ignored. This eliminates delays in decision-making, keeping the project ticking along.
Adhering to the laid-out communication guidelines enhances transparency and accountability. This goes a long way towards strengthening trust and bond among team members. Moreover, when updates, feedback, and issues are communicated professionally, everyone feels valued. This can encourage open discussion and problem-solving.
5.Minimize interruptions
Many communication platforms have default settings for notifications. When employees use multiple channels for workplace communication, they could be bombarded with frequent notifications, leading to fatigue and communication overload.
A communication policy can outline priority levels for different types of communication. It may also encourage employees to prioritize urgency and relevance, when interacting with team members. This can significantly reduce the number of messages exchanged through platforms, avoiding excessive notifications.
Moreover, the policy may require employees to respect work hours and time zones of others. For example, an effective policy should encourage employees not to send messages to colleagues on “don’t disturb” mode. This minimizes interruptions, allowing employees to focus on work.
Challenges You May Face When Implementing a Communication Policy
The process of implementing a communication policy in your organization may not always be smooth. Some employees may be reluctant to change, while others may inconsistently adhere to the policy. When you understand these challenges beforehand, you will be ready to address them for a successful transition.
1. Resistance to change
A study indicates that 37% of employees are resistant to changes within the organization. Employees may be reluctant to follow the new communication policies, especially if they are used to the old ways of sharing information. This may be due to:
- Comfort in existing methods: For example, employees who’re using Slack for all communication may be uncomfortable switching to ClickUp for task tracking.
- Fear of increased workload: Some of your employees will view a new policy as an extra burden that requires them to use new tools and stricter rules.
- Lack of understanding: If employees don’t understand the reason behind the policy changes, they may resist them naturally.
- Phobia of new software: When you introduce a new software, some employees may feel anxious for the fear of the unknown. This may make them reluctant to adapt to the new communication policy.
How to overcome employee pushbacks.
- Explain the benefits of the new communication policy to your employees.
- Engage employees in making decisions to foster a sense of ownership.
- Train employees on new communication guidelines and practices.
- Introduce the new communication policy in a phased approach.
2. Inconsistent adherence
Employees may follow the new communication policy inconsistently. Let’s say the new policy requires teams to use instant messaging for quick updates. If some employees stick to the old habits of sharing updates on email, important information may be lost or missed. This can lead to delays in decision-making, workflow bottlenecks, and frustration among team members.
Inconsistent adherence occurs due to a lack of awareness. If some employees haven’t understood the new policy, adherence issues are bound to happen. Moreover, if employees are accustomed to outdated communication habits, they may struggle to stick to the new rules.
How to overcome inconsistent adherence
- Provide proper training to make all guidelines clear
- The managers or team leaders should lead by example
- Provide structured onboarding for new hires
- Implement regular policy reminders
3.Evolving Communication Trends
Another challenge you may encounter is keeping up with evolving communication trends. For example, the rise of instant messaging apps and AI-driven communication tools means employees may prefer faster, more informal channels over traditional emails. If a policy does not account for these shifts, employees might default to unapproved or insecure platforms, creating gaps in adherence.
Additionally, trends like asynchronous communication require policies to be more flexible. This ensures that remote employees across time zones collaborate effectively without the pressure of immediate responses.
How to overcome it
- Monitor emerging trends, gather employee feedback, and refine policies to keep up with the modern workplace.
- Regularly review and update your communication policy
8 Steps to Develop a Communication Policy

Here are the key steps for coming up with an effective communication policy.
Step 1: Identify the purpose of the policy
Start by identifying the reasons you need the communication policy. To that end, consider the specific goals and challenges your organization aims to address. Some of the steps you can take to identify the purpose, include:
Determine Key Communication Challenges
Ask:
- Are employees using too many unapproved channels, leading to lost information?
- Do delays in responses slow down decision-making?
- Are there security risks, such as sharing sensitive data through insecure platforms?
- Do remote/hybrid teams struggle with asynchronous communication?
Align with Organizational Goals
Your policy should support business objectives, culture, and workflow needs. For example:
- A customer-facing company may focus on response times and professionalism.
- A remote-first organization may prioritize tool usage, time zones, and async collaboration.
Ensure Compliance & Security
Consider legal and security requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, or industry regulations. If your company handles sensitive data, the policy must outline secure communication protocols to prevent data breaches.
Define the Core Purpose Statement
Once challenges and goals are clear, summarize the policy’s purpose in a simple statement. For example:
“This communication policy ensures that all employees use appropriate channels for clear, professional, and secure interactions, enhancing teamwork, productivity, and compliance with data protection laws.”
Step 2: Determine the scope
Next, define the scope of your communication policy. This helps ensure clarity on who the policy applies to, what it covers, and how it should be applied. Here’s how to determine its scope:
Consider All Employee Categories
Identify the different groups within your organization who will be affected by the policy, such as:
- Full-time & Part-time Employees – Regular staff who require communication guidelines for daily work.
- Remote & Hybrid Workers – Employees who may follow different rules for asynchronous communication.
- Contractors & Freelancers – External team members who need limited access to company communication tools.
- Executives & Managers – Leaders who must set the standard for following the policy.
Determine External Stakeholders
Consider whether the policy extends to non-employees, such as:
- Clients & Vendors – If they need to follow specific communication protocols (e.g., secure emails, scheduled calls).
- Third-party Partners – Agencies, consultants, or outsourced teams handling sensitive company information.
Assess Department-Specific Needs
Different teams may require tailored rules:
- Customer Support – Guidelines for handling customer inquiries and response times.
- IT & Security Teams – Policies on secure communication and incident reporting.
- Sales & Marketing – Best practices for external messaging and branding consistency.
Step 3: Choose communication channels
The next step is to specify communication channels for different interactions. For example:
- For team daily standups and quick updates, use Slack and Microsoft Teams. Employees can post a short update on the Slacks’ standup channel each morning. The post should state what they worked on yesterday, any roadblocks they encountered, and the plan they had for the day. This keeps all employees informed without the need for a meeting.
- For project and task management, use Asana or Trello. A project manager can assign tasks, give deadlines, and add comments to the Asanas’ project board. This ensures every employee stays on track without overloading inboxes.
- For external communications, use Zoom and Google Meet. A consulting agency may schedule a weekly client Zoom check-in. Zoom video calls allow face-to-face communication, which may create a stronger client relationship through deep discussions.
Step 4: Set communication guidelines
Come up with clear rules that will govern how your employees will use the communication channels.
- Define the tone and language: You can ask your employees to use a friendly tone and language when writing emails and messages.
- Response time: Set a reasonable timeframe for responding to messages, client inquiries, and concerns.
- Security protocols: Outline the measures each employee must take when handling sensitive information.
Step 5: Ensure compliance
Ensure your communication policy aligns with the legal and regulatory requirements in your country. For example, you may have these key laws:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) if your organization deals with the personal data of EU and EEA citizens. The law will define how your employees safely handle clients’ information through encryption and access control. It will also specify rules for data retention and disposal.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) to ensure confidentiality when handling patients’ health information. The law prohibits employees from sharing patients’ health details through insecure channels like personal emails.
- Whistleblower Protection Laws such as the Dodd-Frank Act in the USA protect employees who report organizations’ unethical practices. The law allows employees to report incidents anonymously.
Step 6: Define roles and expectations
Clearly state who is responsible for ensuring employees follow the policy. Determine who will manage the communication channels and oversee policy enforcement. Also, define who employees will report to in case of misconduct. Some of the roles include:
- All Employees: Follow the communication policy, use approved tools, and maintain professionalism.
- Managers & Team Leads: Ensure team members comply, set response expectations, and resolve communication challenges.
- Executives & Leadership: Model best practices, communicate company-wide updates, and reinforce the policy’s importance.
- IT & Security Teams: Maintain secure communication channels, monitor compliance, and provide training on data security.
- HR Department: Oversee policy enforcement, train new hires, and handle communication-related concerns.
- Customer Support & Sales Teams: Follow protocols for external messaging, client communication, and response times.
Step 7: Roll out the new policy
You can now draft the policy document and share it with top management. If they approve it, publish it and share it with your employees. Include the policy in your new-hire onboarding checklist. This will help new employees acquaint themselves with your communication methods from the word go.
The policy should also be available on your internal knowledge base. This makes it easy for employees to easily access, reference, and follow the communication guidelines. It helps employees find answers on their own, reducing repetitive questions to HR or IT. Moreover, send periodic reminders or notifications when updates are made.
Conclusion
A well-structured communication policy is the pillar of clear, consistent and professional communication within your organization. It helps set expectations, enhance teamwork, and ensure compliance with legal standards. When you properly implement a communication policy, you foster a culture of transparency, accountability, and collaboration within your organization.
However, your communication policy should not be static. As technology evolves and work dynamics change, ensure you regularly review and update it. This will help the policy stay relevant and effective, contributing to the success of your organization.
Have you implemented a communication policy in your organization? What steps did you take to ensure everyone adheres to it? Do you regularly review and update your policy? Share your comments below and let us know your views or any questions regarding your communication policy.
FAQs
Why is communication policy important in an organization?
A communication policy is important because it ensures clear, consistent, and professional communication within your organization.
How often should you update a communication policy?
You should review your communication policy at least once a year or whenever significant technological, legal, or company structure changes happen.
How can you ensure employees adhere to the communication policy?
To ensure employees adhere to the communication policy, train them and regularly remind them of the policy. You should also set clear consequences for violating the policy.




